New Publication: A Promising Anti-Arrhythmic Therapy Targeting RyR2 Tested in the Human Heart
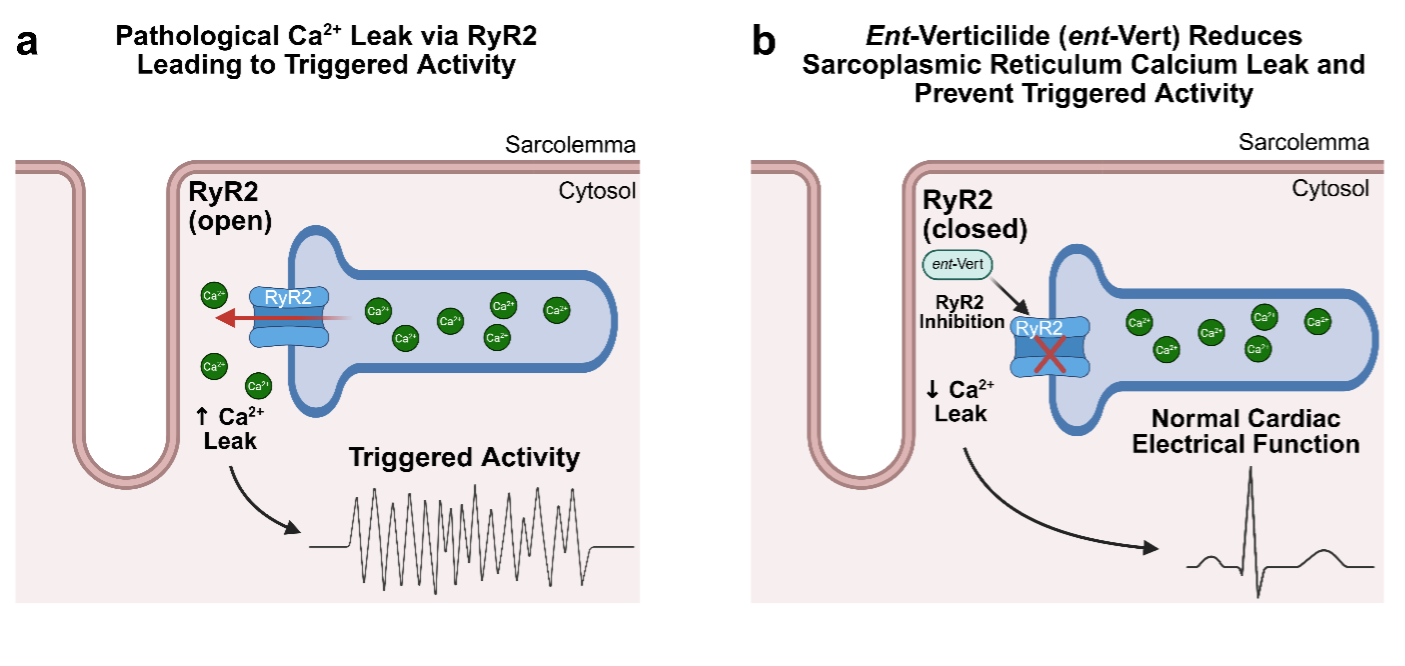
We’re excited to share our newest publication in Journal of Physiology, highlighting a novel anti-arrhythmic therapy, ent-Verticilide, investigated directly in the adult human heart tissue. In collaboration with Vanderbilt University’s E-C Coupling & Cardiac Arrhythmia Lab (led by Bjorn Knollmann), we show that ent-Verticilide safely suppresses abnormal electrical activity by selectively targeting the cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR2).
Unlike existing therapies that can cause off-target side effects, ent-Verticilide modulates only the cardiac isoform of the ryanodine receptor, RyR2, offering a more targeted strategy to prevent life-threatening arrhythmias. This work highlights an important step toward safer, human-relevant anti-arrhythmic treatments.
First author Dr. Micah Madrid and PhD candidate Katy Trampel contributed to this study.